|
|
| Compound | Magnolol |
| Animal species | rat |
| Metabolism parameters | |
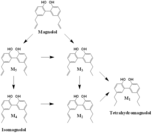
| Metabolites |
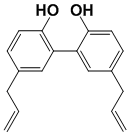
Magnolol
(E)-5-allyl-5'-(prop-1-en-1-yl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2,2'-diol 5-allyl-5'-propyl-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2,2'-diol Isomagnolol (E)-5-(prop-1-en-1-yl)-5'-propyl-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2,2'-diol Tetrahydromagnolol |
| Crude drug | Magnolia Bark |
| References | 1) Hattori M., Sakamoto T., Endo Y., Kakiuchi N., Kobashi K., Mizuno T. and Namba T.: Metabolism of magnolol from Magnoliae Cortex. I. Application of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to the analysis of metabolites of magnolol in rats. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 32, 5010-5017 (1984). 2) Hattori M., Endo Y., Takebe S., Kobashi K. and Namba T.: Metabolism of Magnoliae Cortex. II. Absorption, metabolism and excretion of [ring-14C] magnolol in rats. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 34, 158-167 (1986). 3) Ma Y. H., Ye J. N., Fukasaku N., Hattori M. and Namba T.: Metabolism of magnolol from Magnoliae Cortex. IV. Enterohepatic circulation and gastrointestinal excretion of [ring-14C]- magnolol in rats. Shoyakugaku Zasshi, 42, 130-134 (1988). |
| Remarks | ※Administration of magnolol to rats A suspension of magnolol in arabic gum (2 ml, 25 mg/ml) was orally administered daily (at 4:30 p.m.) to the rats (10 male, Wistar rats, 4 weeks of age, weighing 218-252 g) for 6d. During the experiments, food and drinking water were allowed ad libitum. The feces and urine excreted were collected daily (at 4:30 p.m.). [Hattori et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull., 32, 5010-5017 (1984)] ※Isolation of the fecal metabolites The feces (24-50 g), which had been collected at 24-h intervals after the administration of magnolol, were extracted three times with MeOH (200 ml) and the solution was concentrated in vacuo. The residue was suspended in water (200 ml) and extracted three times with benzene (200 ml), which was then evaporated off in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in CHC13 (10 ml) and applied to a column of alumina (Merck, Art. 1077, 100g). The column was washed with MeOH (100ml) and eluted with BuOH-AcOH-H2O (3:1:1). The eluate was evaporated to dryness in vacuo, dissolved in ether (200 ml) and washed three times with 5% Na2CO3 (100 ml), then dried over Na2SO4. The solution was concentrated, and the residue was dissolved in CHCl3-MeOH (1:1) and adsorbed on C-18 SEP-PAK (Waters Associates, Milford, Mass.), which was eluted with CH3CN-H2O (1:1). The eluate was evaporated to dryness in vacuo, and the residue was dissolved in MeOH (1.0 ml). The solution was repeatedly chromatographed on TSK-ODS-120A (25 cm x 7.2 mm i.d.) at a pressure of 110 kg/cm2. The metabolites, Ml, M2, M3, M4, M5 and M6, were isolated and the structures were determined on the basis of the physical properties and direct comparison with authentic samples. [Hattori et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull., 32, 5010-5017 (1984)] ※Incubation of magnolol with rat feces Fresh feces (1 g) of rats were suspended in 104 volumes of dilution medium. An aliquot (0.3 ml) of the suspension was added to GAM broth (10 ml) containing 0.13 mg of magnolol and anaerobically incubated at 37 °C for 48 h. The culture was then extracted three times with benzene (10 ml). The benzene layer was evaporated to dryness in vacuo and the residue was dissolved in MeOH (0.3 ml). A 2 m1 aliquot of the methanolic solution was then analyzed by HPLC and LC-MS. |

