|
|
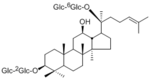
| 化合物名 | Ginsenoside Rb1 |
| 動物種 | 通常ラット、無菌ラット |
| 代謝パラメータ | |
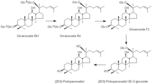
| 代謝物 |
Ginsenoside Rb 1
Ginsenoside Rd Ginsenoside F2 (20S)-Protopanaxadiol 20-O-glucoside (20S)-Protopanaxadiol |
| 関連生薬 | 人参 |
| 参考文献 | 1) Akao T., Kida H., Kanaoka M., Hattori M. and Kobashi K.: Intestinal bacterial hydrolysis is required for the appearance of compound K in rat plasma after oral administration of ginsenoside Rb1 from Panax ginseng. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 50, 1155-1160 (1998). 15) Han Min, Fu Shao, Fang Xiao-ling, Comparison between the characteristics of absorption and pharmacokinetic behavior of ginsenoside Rg1 and ginsenoside Rb1 of Panax notoginseng saponins. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica(薬学学報), 42, 849-853 (2007). Xiaoyu Li, Jianguo Sun, Guangji Wang, Haiping Hao, Yan Liang, Yuanting Zheng, Bei Yan and Longsheng Sheng, Simultaneous determination of panax notoginsenoside R1, ginsenoside Rg1, Rd, Re and Rb1 in rat plasma by HPLC/ESI/MS: platform for the pharmacokinetic evaluation of total panax notoginsenoside, a typical kind of multiple constituent traditional Chinese medicine. Biomedical Chromatography, 21: 735–746 (2007). DOI: 10.1002/bmc.813 22) Gui-feng Deng, Ding-li Wang, Ming-xin Meng, Fan Hu, Tong-wei Yao, Simultaneous determination of notoginsenoside R1, ginsenoside Rg1, Re, Rb1 and icariin in rat plasma by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography B, 877: 2113–2122 (2009). 4) Jun Iwabu, Junko Watanabe, Kazuhiro Hirakura, Yoshinori Ozaki, and Kazuhiro Hanazaki, Profiling of the compounds absorbed in human plasma and urine after oral administration of a traditional Japanese (Kampo) medicine, Daikenchuto. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 38: 2040–2048 (2010). 8) Houfu Liu, Junling Yang, Feifei Du, Xiumei Gao, Xutao Ma, Yuhong Huang, Fang Xu, Wei Niu, Fengqing Wang, Yu Mao, Yan Sun, Tong Lu, Changxiao Liu, Boli Zhang, and Chuan Li, Absorption and disposition of ginsenosides after oral administration of Panax notoginseng extract to rats. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 37: 2290–2298 (2009). |
| 論文備考 | ・Animals, treatment and sampling Male Wistar germ-free rats (WA/Jic, 5-6 weeks; CLEA Japan, Tokyo, Japan) were individually maintained in metabolic cages under germ-free conditions and fasted overnight before the experiments. Autoclaved water and sterilized standard laboratory chow (CE-2, X-ray-treated, CLEA, Japan) were freely available. Six germ-free rats were infected with Eubacterium sp. A-44 (2 mL medium cultured overnight) on the first and third days to produce the gnotobiote rats. One week later sterile ginsenoside Rb1 dissolved in pure water was administered orally to six germ-free rats and to the gnotobiote rats at a dose of 200 mg kg-1. The cumulative faeces were collected 7 h (three rats) and 15 h (three rats) after administration. Blood samples from the abdominal vein and the gastrointestinal tract were taken under pentobarbital anaesthesia 7 h (three rats) and 15 h (three rats) after administration. Plasma samples were prepared by centrifugation of the heparinized blood and stored at -20°C until use. [Akao et al., J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 50, 1155-1160 (1998)] |

