|
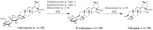
|
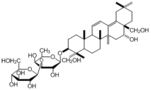
| 化合物名 | Saikosaponin b1 |
| 動物種 | ヒト腸内細菌フローラ |
| 代謝パラメータ |
Oral administration
Oral administration Oral administration Oral administration Oral administration Oral administration Oral administration Oral administration Oral administration |
| 代謝物 |
Saikosaponin b1
Prosaikogenin A Saikogenin A |
| 関連生薬 | 柴胡 |
| 参考文献 | 1) Kida H., Nakamura N., Meselhy M. R., Akao T. and Hattori M.: Isolation and identification of human intestinal bacteria capable of hydrolyzing saikosaponins. J. Trad. Med., 14, 34-40 (1997). 2) Kida H., Akao T., Meselhy M. R. and Hattori M.: Enzymes responsible for the metabolism of saikosaponins from Eubacterium sp. A-44, a human intestinal anaerobe. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 20, 1274-1278 (1997). 3) Kida H., Akao T., Meselhy M. R. and Hattori M.: Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of orally administered saikosaponin b1 in conventional, germ-free and Eubacterium sp. A-44 infected gnotobiote rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 21, 588-593 (1998). |
| 論文備考 | ※Preparation of a bacterial suspension of human feces Fresh feces obtained from a healthy young man (age : 25, male) were suspended in five volumes of phosphate buffer (pH 7.2). The fecal suspension thus obtained was used in the following experiments. [Kida et al., J. Trad. Med., 14, 34-40 (1997)] ※Time course of the metabolism of saikosaponin b1 by an intestinal bacterial suspension GAM broth (9 ml) containing saikosaponin b1 (a final concentration, 1 mM) was incubated with an intestinal bacterial suspension (1 ml) in an anaerobic incubator at 37°C. A 100 μm portion was taken out at intervals (4, 10, 24 and 48 hours) and extracted with BuOH (100 μl). Five micro liters of the BuOH layer were applied to a TLC plate, which was developed with solvent system A. [Kida et al., J. Trad. Med., 14, 34-40 (1997)] |

