|

|
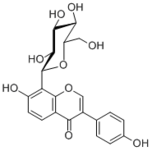
| Compound | Puerarin |
| Animal species | human intestinal bacteria |
| Metabolism parameters | |
| Metabolites |
Puerarin
Daidzein Dihydrodaidzein (-)-Equol |
| Crude drug | Pueraria Root |
| References | 1) Jin J. S., Nishihata T., Kakiuchi N. and Hattori M.: Biotransformation of C-glucosyl- isoflavone puerarinto estrogenic (3S)-equol in co-culture of two human intestinal bacteria. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 31, 1621-1625 (2008). 2) Nakamura K., Nishihata T., Jin J. S., Ma C. M., Komatsu K., Iwashiro M., and Hattori M.: The C-glucosyl bond of puerarin was cleaved hydrolytically by a human intestinal bacterium strain PUE to yield its aglycone daidzeine and intact glucose. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 59, 23-27 (2011). 3) Jin J. S., Kitahara M., Sakamoto M., Hattori M., and Yoshimi Benno Y.: Slackia equolifaciens sp. nov., a human intestinal bacterium capable of producing equol. Int. J. System. Evol. Microbio., 60, 1721-1724 (2010). |
| Remarks | ※A, transformation of puerarin to daidzein by strain PUE; B, transformation of daidzein to equol by strain DZE; C, transformation of puerarin to equol by a mixture of strain PUE and DZE. Other peaks except puerarin, daidzein, and equol were identified as ingredients of GAM broth through analysis of incubation samples in the absence of substrates. STD, standards. ※Bacterial Incubation and analysis of metabolites Each bacterium was picked up from GAM agar plates and inoculated into 2 ml of GAM broth. When turbidities (540 nm) of bacterial suspensions reached 1.96±0.09 optical density (O.D.) (strain PUE) and 0.30±0.02 O.D. (strain DZE), a 100-μl portion of the precultured bacteria was inoculated into 2 ml of GAM broth with substrates. After incubation, a 100-μl aliquot was removed and extracted three times with 200 μl of BuOH. After evaporation of the BuOH in vacuo, the residue was dissolved in 0.3 ml of MeOH. The MeOH solution was filtered through a 0.2-μm membrane filter, and a 10-μl portion was injected onto a column for HPLC analysis. ※LC/MS Analysis HPLC was performed on an Agilent 1100 system (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany) with a photodiode array detector and Agilent 1100 series binary pump, and an Esquire 3000plus mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltonic GmbH, Bremen, Germany) coupled with an ESI interface and an ion trap mass analyzer. Analysis of puerarin, daidzein, and equol was performed under the following conditions: column, TSK-gel ODS-80Ts (Tosoh Co., Tokyo, Japan, 4.6 mm × 150 mm); mobile phase, H2O (solvent system A) and CH3CN (solvent system B) in a gradient mode (B from 15 to 50% in 20 min); flow rate, 1.0 ml/min; detection, UV 280 nm; temperature, 30°C. High-purity nitrogen was used as dry gas at a flow rate at 10 L/min, dry temperature at 360°C. Helium was used as nebulizer at 50 psi. The electron spray ionization (ESI) interface and mass spectrometric parameters were optimized to obtain maximum sensitivity. |

