|
|
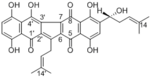
| Compound | Shikonin |
| Animal species | human intestinal bacteria Bacteroides fragilis subsp. thetaotus, Eubacterium sp. A-44 |
| Metabolism parameters | |
| Metabolites |
Shikometabolin A
Shikometabolin B Deoxyshikonin Anhydroshikonin Shikonin (R)-5,8-dihydroxy-6-(1-hydroxy-4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl)naphthalene-1,4-dione Cycloshikonin Metaboshikonin I Metaboshikonin II Shikometabolin C Shikometabolin D Shikometabolin E |
| Crude drug | Lithospermum Root |
| References | 1) Meselhy M. R., Kadota S., Tsubono K., Kusai A., Hattori M. and Namba T.: Shikometabolins A, B, C and D, novel dimeric naphthoquinone metabolites obtained from shikonin by human intestinal bacteria. Tetrahedron Lett., 35, 583-586 (1994). 2) Meselhy M. R., Kadota S., Tsubono K., Hattori M. and Namba T.: Biotransformation of shikonin by human intestinal bacteria. Tetrahedron, 50, 3081-3098 (1994). 3) Meselhy M. R., Nishimoto E., Akao T. and Hattori M.: Transformation of shikonin by a cell-free extract of Eubacterium sp. A-44, a human intestinal bacterium. J. Trad. Med., 18, 58-63 (2001). |
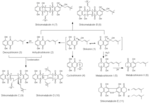
| Remarks | ※Transformation of shikonin (1) with Bacteroides fragilis subsp. thetaotus Stock cultures of B. fragilis (2 1) were added to GAM broth (18 1) and cultured overnight at 37 °C under anaerobic conditions. The bacterial culture was centrifuged at 7,800 x g for 10 min and the pellets were washed twice with saline and suspended in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (20 1, pH 7.3). A total of 20 g of shikonin (1, in 200 ml DMSO) was added to the bacterial suspension and the mixture was anaerobically incubated for 3 d at 37 °C. The mixture was pooled, adjusted to pH ca. 3.0 with 5% HC1, and extracted with EtOAc (201 x 5). The EtOAc layer was washed with H2O and evaporated in vacuo to give a dark brown residue (34 g). The residue was applied to a silica gel column (50 x 10 cm ), which was then gradiently eluted with hexane, CHCl3 and CHCl3-MeOH (9 : 1), successively. Fractions (1500 ml each) were collected and monitored by TLC. Fraction A was concentrated and applied to a Kieselgel 60 (E. Merck) column. Elution with hexane: Me2CO (9:1) gave three compounds 2, 3 and 4. Fraction B was subjected to column chromatography [Kieselgel 60, hexane-CHCl3 (7 : 3 and 1 : 9)] and subsequent preparative-TLC (solvent system A) to afford compounds 5 and 6 as main yellow and orange powder, respectively, with minor compounds 9-11. Successive elution of the EtOAc extract with CHCl3-MeOH (9:1) afforded a mixture of dark blue compounds in fraction C which could not be separated by HPLC. However, repeated column chromatography over Kieselgel 60 [hexane-CHCl3 (1 : 9) and CHCl3-MeOH (9 : 1)], preparative-TLC and subsequent Sephadex LH-20 [CHCl3-MeOH (7 : 3)] column chromatography afforded two main dark blue compounds 7 and 8. [Meselhy et al., Tetrahedron, 50, 3081-3098 (1994)] ※Shikonin (1, 5 mg each) was incubated with a precultured bacterial suspension of B. fragillis (10 ml each) for 3 days under anaerobic conditions. The incubation mixtures were taken at 12 h intervals, adjusted to pH ca. 3 and extracted with EtOAc (10 ml x 3). The EtOAc extract was evaporated in vacuo to give a residue. The residue was dissolved in MeOH (1 ml) and analyzed by HPLC. [Meselhy et al., Tetrahedron, 50, 3081-3098 (1994)] ※Crude enzyme preparation and transformation of shikonin (1) Eubacterium sp. A-44 has been previously isolated from human feces, and was maintained in GAM broth medium. Twenty ml of the culture were transferred to 10 volumes of the medium and incubated for 18 hr in an anaerobic incubator. The bacterial cells were harvested by centrifugation at 1500 × g for 10 min, and the pellets were suspended in 50 mM K-phosphate buffer (pH 7.3, 90 ml). The bacterial cells were disrupted by sonication (60 sec × 2), and part of the sonicated bacterial suspension (30 ml) was further centrifuged at 22500 × g for 30 min to obtain a bacterial cell-free extract, supernatant, which was kept on ice and used as the crude enzyme preparation. Ultracentrifugation of the supernatant (6 ml) at 3000 × g (for 45, 15 and 15 min) was carried out using Centriprep-10. Shikonin (1, 50 mg in 1 ml DMSO) was added to the sonicated bacterial suspension (60 ml) and the reaction mixture was incubated in an anaerobic incubator for 2 hr. After acidification with 1 N HCl (pH 5.0), the reaction mixture was extracted with EtOAc (200 ml × 5). The EtOAc layer was washed with H2O, dried over MgSO4 and then evaporated in vacuo to give a residue. The residue was applied to a column of silica gel. Elution was started with hexane-Me2CO (9: 1→7: 3) and then CHCl3 with increasing % of MeOH to give 46 fractions. Fr. 2-8 afforded 3 (6 mg) and 4 (4 mg), 2 (18 mg) was obtained from Fr. 17-21, while 5 (4 mg) and 6 (4 mg) were from Fr. 42-46. [Meselhy et al., J. Trad. Med., 18, 58-63 (2001)] |

