|
|
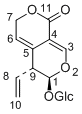
| Compound | Gentiopicroside |
| Animal species | human intestinal microflora, human intestinal bacteria Veillonella parvula |
| Metabolism parameters | |
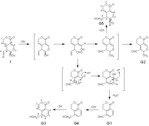
| Metabolites |
Gentiopicroside
(6R)-6-hydroxy-5-vinyl-5,6-dihydropyrano[3,4-c]pyran-1(3H)-one (E)-2-(3-(hydroxymethylene)-2-oxo-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-4-yl)but-3-enal 3-methyl-8-oxo-3,4,6,8-tetrahydropyrano[3,4-c]pyran-4-carbaldehyde (5S,6S)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-6-methyl-5,6-dihydropyrano[3,4-c]pyran-1(3H)-one 3-methyl-8-oxo-3,5,6,8-tetrahydropyrano[3,4-c]pyran-4-carbaldehyde 2-oxo-4-(1-oxobut-3-en-2-yl)-5,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-3-carbaldehyde 8-hydroxy-1-oxo-3,4,7,8-tetrahydro-1H-isochromene-5-carbaldehyde 1-oxoisochroman-5-carbaldehyde 5-(hydroxymethyl)isochroman-1-one 5-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-isochromen-1-one |
| Crude drug | Gentian , Swertia Herb |
| References | 1) El-Sedawy A. I., Hattori M., Kobashi K., and Namba T.: Metabolism of gentiopicroside (gentiopicrin) by human intestinal bacteria. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 37, 2435-2437 (1989). |
| Remarks | ※Each bacterium was cultured in the presence of gentiopicroside (1) for 24 h at 37 °C. The products were extracted with EtOAc and analyzed by TLC-densitometry. The peaks corresponding to metabolites are represented by G—G5; other peaks originate from the bacterial cells and culture broth. The Rf values of these metabolites on TLC with CHCl3-MeOH (15:1) were as follows: G1, 0.92; G2, 0.85; G3, 0.59; G4 and G5, 0.46—0.50. ※Screening of intestinal bacterial strains for ability to metabolize gentiopicroside (1) Each precultured bacterial strain (0.2 ml) was added to GAM broth (10 ml) and cultured for 24 h at 37 °C under anaerobic conditions. Gentiopicroside (1) was added to each culture, and the mixturewas incubated for 22 h under the same conditions and then extracted with EtOAc (10 ml). After evaporation of the EtOAc, CHCl3-MeOH (1:1, 0.5 ml) was added to the residue and an aliquot (50 μl) of the solution was applied to a silica gel TLC plate, which was developed with CHCl3-MeOH (15:1). The metabolites separated on the plate were quantitatively analyzed with a TLC scanner at 230 nm relative to a reference wavelength of 550 nm. [El-Sedawy et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull. 37, 2435-2437 (1989)] ※Isolation of metabolites A precultured bacterial suspension (100 ml) of Veillonella parvula ss parvula ATCC 10790 was added to GAM broth (900 ml) and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C in an anaerobic jar, in which air had been replaced with O2-free CO2 in the presence of steel wool. [El-Sedawy et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull. 37, 2435-2437 (1989)] ※Gentiopicroside (1, 1 g in 5 ml of 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.4) was then added, and the mixture was anaerobically incubated for 22 h at 37 °C and extracted 3 times with EtOAc (1000 ml each). The combined solutions were concentrated in vacuo to give an oily residue. The residue was applied to a column of silica gel, which was washed with hexane and eluted successively with benzene, benzene-CHCl3 (3:1) and benzene-CHCl3 (2:1) to afford five metabolites, G1 (3 mg), G2 (3 mg), G3 (14 mg) and G4 + G5 (12 mg). Repeated preparative TLC of a mixture of G4 and G5 gave two pure compounds. [El-Sedawy et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull. 37, 2435-2437 (1989)] |

