|
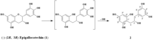
|
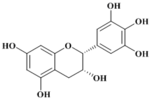
| Compound | Epigallocatechine |
| Animal species | human intestinal bacteria Eubacterium sp. strain SDG-2 |
| Metabolism parameters | |
| Metabolites |
(-)-(2R, 3R)-Epigallocatechin
(S)-5-(2-hydroxy-3-(2,4,6-trihydroxyphenyl)propyl)benzene-1,2,3-triol (S)-2-(3-(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxypropyl)benzene-1,3,5-triol |
| Crude drug | Crataegus Fruit , Ephedra Herb |
| References | 1) Wang L., Meselhy M. R., Li Y., Nakamura N., Min B., Qin G. and Hattori M.: The heterocyclic ring fission and dehydroxylation of catechins and related compounds by Eubacterium sp. strain SDG-2, a human intestinal bacterium. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 49, 1640-1643 (2001). |
| Remarks | ・Incubation of (-)-epigallocatechin (1) with Eubacterium sp. strain SDG-2 (-)-Epigallocatechin (1) (30 mg each in 2 ml MeOH) was added to a bacterial suspension and incubated anaerobically for 36 h. The respective reaction mixtures were then treated as usual to give 2 (12 mg). [Wang et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull., 49, 1640-1643 (2001)] |

