|
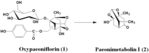
|
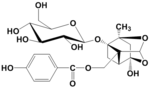
| Compound | Oxypaeoniflorin |
| Animal species | human intestinal microflora |
| Metabolism parameters | |
| Metabolites |
Oxypaeoniflorin
Paeonimetabolin I |
| Crude drug | Moutan Bark , Peony Root |
| References | 1) Hattori M., Shu Y. Z., Shimizu M., Hayashi T., Morita N., Kobashi K., Xu G. J. and Namba T.: Metabolism of paeoniflorin and related compounds by human intestinal bacteria. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 33, 3838-3846 (1985). 2) Shu Y. Z., Hattori M., Akao T., Kobashi K., Kakei K., Fukuyama K., Tsukihara T. and Namba T.: Metabolism of paeoniflorin and related compounds by human intestinal bacteria. II. Structures of 7S- and 7R-paeonimetabolins I and II formed by Bacteroides fragilis and Lactobacillus brevis. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 35, 3726-3733 (1987). |
| Remarks | ※Incubation of oxypaeoniflorin (1) with an intestinal bacterial mixture Oxypaeoniflorin (1, 600 mg) dissolved in EtOH (4 ml) was added to a human intestinal bacterial mixture (600 ml). The mixture was anaerobically incubated at 37 °C for 24 h and extracted three times with AcOEt (600 ml each). The AcOEt phase was concentrated to a small volume in vacuo. The mixture thus obtained was applied to a silica gel column (68 g, 2.4 cm i.d. x 27cm). The column was washed with benzene and then eluted with CHCl3. Fractions of 50 ml/flask were collected and monitored by silica gel TLC. Fractions 15-24 were pooled and evaporated to dryness in vacuo. The residue (68 mg) was purified by re-chromatography (silica gel, 30 g; column size, 1.9 cm i.d. x 16 cm). A pure oily compound was eluted with CH2Cl2-AcOEt (100:3); yield, 32 mg (13%). This compound was identical with paeonimetabolin I (2) obtained from paeoniflorin based on a comparison of the Rf values in various solvent systems and the IR spectra. [Hattori et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull., 33, 3838-3846 (1985).] |

