|

|
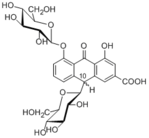
| Compound | Rheinoside C, D |
| Animal species | human intestinal microflora |
| Metabolism parameters | |
| Metabolites |
Rheinoside C
8-Deglucosylrheinoside C Rhein anthrone |
| Crude drug | Rhubarb |
| References | 1) 牧野圭吾修士論文『ヒト腸内細菌によるanthrone及びoxyanthrone C-配糖体のC-グルコシル結合の開裂について』 (2000) 富山医科薬科大学. |
| Remarks | ※Metabolism of rheinosides C and D by human intestinal flora A fecal bacterial suspension (0.5 ml) precultured for 24 h was inoculated into PYF broth (4.5 ml) containing 2 mM rheinoside C or D, and the mixture was anaerobically incubated for 24 h. ※Quantitative determination of rheinosides and 8-deglucosylrheinosides A 50 μl portion of the culture and 50 μl of MeOH containing 0.1% AcOH were vigorously stirred and centrifuged at 8800 x g for 1 min to separate a supernatant and precipitates. A portion of the supernatant was applied to a normal phase TLC plate of silica gel and developed with a mixed solvent CHCl3-MeOH-H2O (6 : 4 : 1). The spots of rheinoside and 8-deglucosylrheinoside were quantitatively determined by TLC-densitometry at a wavelength of 350 nm. ※Quantitative determination of rhein anthrone A 50 μl portion of the culture, 20 μl of 1% N, N-dimethyl-p-nitrosoaniline solution in pyridine and 50μl of BuOH saturated with H2O containing 0.1% AcOH were mixed and centrifuged at 8800 x g for 1 min. A portion of the BuOH phase was spotted onto a polyamide TLC sheet, and developed with CHCl3-MeOH-H2O (7:3:0.5). Rhein anthrone anil was quantitatively determined by TLC-densitometry at 660 nm, using a standard line of an authentic compound. ※Metabolism of 8-deglucosylrheinoside D by Eubacterium sp. BAR A 0.5 ml portion of a bacterial suspension of Eubacterium sp. BAR cultured in GAM broth for 24 h at 37°C was inoculated into PYF broth (4.5 ml) containing 8-deglucosylrheinoside D (final concentration of 1 mM), and the mixture was anaerobically incubated at 37°C. The formation of rhein anthrone was quantitatively monitored by TLC densitometry, after treatment with N, N-dimethyl-p-nitrosoaniline. Bacterial growth was monitored at 540 nm after 10-fold dilution of the culture. |

