Polygonum Root
|
TMPW No.:1222 |
| Synonym | |
| Latin name | Polygoni Multiflori Radix |
| Botanical source: Family name | Polygonaxeae |
| Botanical source: Plant name | Polygonum multiflorum Thunberg (IPNI:927345-1) |
| Part used | Root |
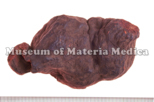
| Empirical criteria for quality selection | The radixes looks like a string of beads. After cutting roots, the cross section of good one is big, pale red and has a flower-like pattern. It has five deep longitudinal grooves on the external (NI). |
| Constituents | Anthraquinones: Chrysophanol, Emodin Tannins: Tannin Stilbenes: 2,3,5,4'-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside Indole alkaloids: Indole-3-(L-α-amino-α-hydroxypropionic acid) methyl ester |
| Pharmacological effects | Enhancing intestinal movement (water extract), suppression of the cholesterol absorption from intestinal tract, and corticotropin like action. |
| Indications | Being tonic, cathartic and enriching blood, it is applied to treat insufficiency of essence and blood, backache with weakness of the knee joint, pollution, leukorrhea, white hair etc. |
| Diseases | Lightheadedness, Bleary eyes, Vertigo, Ear buzzing, Heaviness and powerlessness in lumber and knee, Numbness, Alopecia, Premature gray hair, Spermatorrhea, Chill, Fever, Pyogenic dermatosis, Cervical lymphadenopathy, Itching, Constipation, Hyperlipidemia |
| Formulas | tokiinshi |
| Meridian tropism | Liver, Kidney |
| Property | Warm |
| Flavor | Bitter, Sweet, Astringent |
| Classification in "Shen-non Ben-cao Jing" | |
| TCM: Classification | Tonics |
| TCM: Medicinal effects | To counteract toxicity, to cure carbuncles, and to relax bowels; used for lymphadenitis, carbuncles, urticaria with itching, constipation, and hyperlipemia. |
| Remarks | Listed in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia 18th ed. Baiheshouwu (白何首烏 in CN) is the root of Cynanchum auriculatum Royle of family Asclepiadaceae, C. bungei Dcne. (Koikema in JP), C. wilfordii Hemsl. and other species. |
| References | NI: N. Isshiki, Methods of Quality Evaluation and Preparation of Wakan-yaku, Tohodo Shoten, Tokyo, 1987. |
