|

|
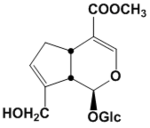
| Compound | Geniposide |
| Animal species | human intestinal microflora, human intestinal bacteriaKlebsiella pneumoniae |
| Metabolism parameters |
Oral administration Oral administration Oral administration Oral administration Oral administration Oral administration |
| Metabolites |
Geniposide
Genipin methyl 2-((1S,2S)-3-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(iminomethyl)cyclopent-3-en-1-yl)-3-oxopropanoate Genipinine |
| Crude drug | Gardenia Fruit |
| References | 1) Kawata Y., Hattori M., Akao T., Kobashi K. and Namba T.: Formation of nitrogen- containing metabolites from geniposide and gardenoside by human intestinal bacteria. Planta Med., 57, 536-542 (1991). 2) H. Lv, H. Sun, W. Sun, L. Liu, P. Wang, X. Wang, H. Cao: Pharmacokinetic studies of a Chinese triple herbal drug formula. Phytomedicine 15, 993–1001 (2008). 3) Zhi-Min Long, Kai-Shun Bi, Yan-Shuang Huo, Xiao-Yu Yan, Xu Zhao, Xiao-Hui Chen: Simultaneous quantification of three iridoids in rat plasma after oral administration of Zhi-zi-chi decoction using LC-MS. J. Sep. Sci., 34, 2854–2860 (2011). 4) Yanqing Sun, Fang Feng and Xiupei Yu: Pharmacokinetics of geniposide in Zhi‐Zi‐Hou‐Pu, decoction and in different combinations of its constituent herbs. Phytother. Res. 26: 67–72 (2012). 5) Xijun Wang, Hui Sun, Aihua Zhang, Guozheng Jiao, Wenjun Sun and Ye Yuan: Pharmacokinetics screening for multi-components absorbed in the rat plasma after oral administration traditional Chinese medicine formula Yin-Chen-Hao-Tang by ultra performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization/quadrupole- time-of-flight mass spectrometry combined with pattern recognition methods. Analyst, 136: 5068-5076 (2011). 6) Y.C. Hou, S.Y. Tsai, P.Y. Lai, Y.S. Chen, P.D.L. Chao.: Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of genipin and geniposide in rats. Food and chemical toxicology, 46: 2764–2769 (2008). 7) Chungang Chen, Fenxia Han, Yan Zhang, Jianfeng Lu and Yuzhong Shi.: Simultaneous determination of geniposide and its metabolites genipin and genipinine in culture of Aspergillus niger by HPLC. Biomed. Chromatogr. 22: 753–757 (2008). |
| Remarks | ※K. pneumoniae was anaerobically cultured in GAM broth (500 ml) for 24 h at 37 °C and the culture was centrifuged at 5700 x g for 5 min. The precipitates were suspended in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.3; 50 ml) and the suspension was divided into tubes (5 ml/tube). Ten mg of 1 was added to each tube and the tubes were anaerobically incubated at intervals at 37 °C. The incubation mixture was extracted with EtOAc (5 ml x 2) and the combined EtOAc solutions were evaporated in vacuo to give a residue. The residue was dissolved in 100 μl of MeOH, and 4 μl of the solution were injected to a column of μS C18 and analyzed by LC/MS. The amounts of the primary aglycones and nitrogen-containing compounds were determined by means of selected ion monitoring (SIM), using calibration lines prepared with authentic samples. [Kawata et al., Planta Med., 57, 536-542 (1991)] ※Feces (10 g) obtained from a healthy man was suspended in 100 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.3; 100ml). Tubes containing 1 (30 mg) and the suspension (10 ml) were anaerobically incubated for 10, 17, and 42 h at 37 °C. The mixture was then extracted with EtOAc (7 ml x 2) and the combined solutions were evaporated in vacuo to give a residue. The residue was dissolved in MeOH (60 μl) and a 1 μl aliquot was analyzed by LC/MS. [Kawata et al., Planta Med., 57, 536-542 (1991)] Pharmacokinetic parameters of geniposide in rat plasma after oral administration of Yin Chen-Hao-Tang preparation Mean±SD Pharmacokinetic parameters of geniposide, 6α-hydroxygeniposide, and genipin gentiobioside determination in rat plasma (n=6) |

