| References |
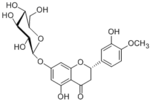
1) Véronique Habauzit, Inge-Lise Nielsen, Angel Gil-Izquierdo, Anna Trzeciakiewicz, Christine Morand, Winnie Chee, Denis Barron, Patrice Lebecque, Marie-Jeanne Davicco, Gary Williamson, Elizabeth Offord, Véronique Coxam and Marie-Noëlle Horcajada: Increased bioavailability of hesperetin-7-glucoside compared with hesperidin results in more efficient prevention of bone loss in adult ovariectomised rats. British Journal of Nutrition, 102, 976–984 (2009). |
| Remarks |
Wistar rats were sham operated or ovariectomised (OVX), then pair fed for 90 d a casein-based diet supplemented or not with freeze-dried orange juice enriched with hesperidin (Hp) or hesperetin 7-glucoside (H-7-glc) at two doses of 0.25 and 0.5 % (hesperetin basis). In the rats fed 0.5%, a reduction in OVX-induced bone loss was observed regarding total bone mineral density (BMD): + 7.0% in OVX rats treated with Hp (HpOVX) and +6.6% in OVX rats treated with H-7-glc (H-7-glcOVX) v. OVX controls (p<0.05). In the rats fed 0.25% diet, the H-7-glc OVX group showed a 6.6% improvement in BMD v. the OVX controls (p<0.05), whereas the Hp diet had no effect at this dose. The BMD of rats fed 0.25% H-7-glc was equal to that of those given 0.5% Hp, but was not further increased at 0.5% H-7-glc. Plasma hesperetin levels and relative urinary excretion were significantly enhanced in the H-7-glc v. Hp groups, and the metabolite profile showed the absence of eriodictyol metabolites and increased levels of hesperetin sulphates. Taken together, improved bioavailability of H-7-glc may explain the more efficient bone protection of this compound. |