|
|
| Compound | Abrusin 2”-O-β-D-apioside |
| Animal species | human intestinal microflora |
| Metabolism parameters | |
| Metabolites |
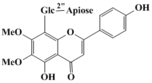
abrusin 2''-O-β-D-apioside
Abrusin 1-(2,6-dihydroxy-3,4-dimethoxy-5-((2R,3R,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)phenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one 1-(2', 6'-Dihydroxyl-3', 4'-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(4''-hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one 5,6-Dimethoxybenzene-1,3-diol 3-(4'-Hydroxyphenyl)propionic Acid 3-Phenylpropionic Acid |
| Crude drug | |
| References | 1) Li Y., Meselhy M. R., Wang L., Ma C., Nakamura N., and Hattori M.: Biotransformation of a C-glycosylflavone, abrusin 2"-O-β-D-apioside, by human intestinal bacteria. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 48, 1239-1241 (2000). |
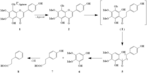
| Remarks | Time course of the transformation of abrusin 2"-O-β-D-apioside (1) Abrusin 2"-O-β-D-apioside (1, 10 mmol in 200 ml DMSO) was added to a human fecal suspension (5%, 3.8 ml) and incubated at 37°C in an anaerobic incubator. Samples were picked up at intervals and extracted with BuOH (saturated with water and acidified with CH3COOH, 200 ml). After centrifugation at 8,800 × g for 5 min, 100 ml of the BuOH layer was evaporated in vacuo to give a residue. The residue was dissolved in MeOH (100 ml) and filtered through a Gelman filter (0.45 μm). The metabolites in the MeOH filtrate were analyzed by HPLC using calibration lines obtained with isolated compounds (5 and 6) or authentic samples (1, 2, 7 and 8). [Li et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull., 48, 1239-1241 (2000)] |

