|
|
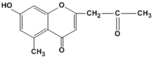
| Compound | Aloesone |
| Animal species | human intestinal microflora |
| Metabolism parameters | |
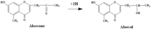
| Metabolites |
Aloesone
Aloesol |
| Crude drug | Aloe |
| References | 1) Che Q. M., Akao T., Hattori M., Kobashi K. and Namba T.: Metabolism of aloesin and related compounds by human intestinal bacteria: A bacterial cleavage of the C-glucosyl bond and the subsequent reduction of the acetonyl side chain. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 39, 704-708 (1991). |
| Remarks | ・Preparation of a bacterial mixture from human feces Fresh feces from a healthy man were thoroughly suspended in 50 volume of 0.2 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.2), filtered through layers of gauze to eliminate the sediment. The filtrate was used as an intestinal bacterial mixture in the following experiments. [Che et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull., 39, 704-708 (1991)] ・Incubation of aloesone with an intestinal bacterial mixture Aloesone (30 mg, 3) in DMSO (0.2 ml) was incubated with an intestinal bacterial mixture (30 ml) for 3 d at 37 °C in an anaerobic box. The incubation mixture was concentrated in vacuo, followed by preparative TLC on silica gel with EtOAc to give dl-aloesol (2) in a yield of 18 mg (59%). [Che et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull., 39, 704-708 (1991)] |

