|

|
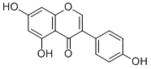
| Compound | Genistein |
| Animal species | human intestinal microflora, human intestinal bacteria DZE |
| Metabolism parameters | |
| Metabolites |
Genistein
3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)chroman-4,5,7-triol 5-Hydroxyequol |
| Crude drug | Pueraria Root , Sophora Japonica Flower , Sophora Subprostrata Root |
| References | 1) Jin J. S., Nishihata T., Kakiuchi N. and Hattori M.: Biotransformation of C-glucosylisoflavone puerarin to estrogenic (3S)-equol in co-culture of two human intestinal bacteria. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 31, 1621-1625 (2008). |
| Remarks | ・Anaerobic incubation with human intestinal bacterium, monitoring a metabolite by HPLC A bacterium was inoculated into 2 ml of GAM broth. When turbidities (540 nm) of the bacterial suspension reached to 0.30±0.02 O.D., a 100-μl portion of the precultured bacteria was inoculated into 2 ml of GAM broth with genistein. After incubation, a 100-μl aliquot was removed and extracted three times with 200 μl of BuOH. After evaporation of the BuOH in vacuo, the residue was dissolved in 0.3 ml of MeOH. The MeOH solution was filtered through a 0.2-μm membrane filter, and a 10-μl portion was injected onto a column for HPLC analysis under the conditions described above. [Jin et al., Biol. Pharm. Bull., 31, 1621-1625 (2008).] ・Preparation of 5-hydroxyeqoul by a human intestinal bacterial strain DZE A bacterial suspension (50 ml) of strain DZE was inoculated to 0.8 l GAM broth containing genistein (50 mg) and incubated at 37˚C in an anaerobic incubator for 120 h. The reaction mixture was then extracted three times with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was evaporated under reduced pressure to give a residue. The residue was applied to a column of silica gel, which was eluted with a solvent system, CHCl3-MeOH (20:1), to give 5-hydroxyequol (24 mg, 50% in yield). [Jin et al., Biol. Pharm. Bull., 31, 1621-1625 (2008).] |

