|
|
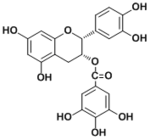
| Compound | Epicatechin 3-O-gallate |
| Animal species | human intestinal microflora, rat intestinal microflora |
| Metabolism parameters | |
| Metabolites |
(-)-epicatechin 3-O-gallate
(2R,3R)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)chroman-3,5,7-triol Gallic acid pyrogallol (S)-2-(3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxypropyl)benzene-1,3,5-triol (S)-2-(2-hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propyl)benzene-1,3,5-triol (R)-5-(3,4-dihydroxybenzyl)dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (R)-5-(3-hydroxybenzyl)dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one 5-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)pentanoic acid 5-(3-hydroxyphenyl)pentanoic acid 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid 5-(3-methoxyphenyl)pentanoic acid 2,3-dihydroxyphenyl 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoate |
| Crude drug | Crataegus Fruit , Rhubarb |
| References | 1) Meselhy M. R., Nakamura N. and Hattori M.: Biotransformation of (-)-epicatechin 3-O-gallate by human intestinal bacteria. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 45, 888-893 (1997). |
| Remarks | ・Incubation of (-)-epicatechin 3-O-gallate (1) with human intestinal bacteria (HIB) (-)-Epicatechin 3-O-gallate (1, 500 mg in 5 ml MeOH) was added to an HIB suspension (500 ml) and incubated at 37 ˚C in an anaerobic incubator for 48 h. The reaction mixture was then extracted with a BuOH-Et2O (1:1) mixture (4 x 500 ml). The organic layer was filtered through anhydrous MgSO4 and evaporated under reduced pressure to give a residue (1.02 g). The residue was subjected to a column of Sephadex LH-20 (30 x 3.0 cm i.d.), the elution being started with EtOH and then EtOH-MeOH with a gradual increase in MeOH. Fractions were pooled to give Fr. A-D. Repeated MPLC (RP-18, MeOH-H2O; 3:7) of Fr. A (32 mg) gave 2 (3 mg), 5 (3 mg) and 6 (2 mg). Fr. B (46 mg) afforded 7 (1 mg), 8 (2 mg) and 12 (3 mg). MPLC (RP-18, MeOH-H2O; 4:6) of Fr. C (59 mg) afforded 3 (2 mg), 4 (5 mg), 9 (14 mg), 10 (15 mg), 12 (9 mg), 13 (5 mg) and 14 (1 mg). CC/RP-2 (50% aq. MeOH) of Fr. D (23 mg) gave an additional amount of 9 (2 mg) and 12 (3 mg). [Meselhy et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull., 45, 888-893 (1997)] |

