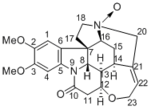
|

|
| Compound | Burcine N |
| Animal species | human intestinal bacteria Lactobacillus acidophilus |
| Metabolism parameters | |
| Metabolites |
Brucine N-oxide
16-Hydroxybrucine Brucine |
| Crude drug | Nux Vomica |
| References | 1) El-Mekkawy S., Meselhy M. R., Kawata Y., Kadota S., Hattori M., and Namba T.: Metabolism of strychnine N-oxide and brucine N-Oxide by human intestinal bacteria. Planta Med., 59, 347-350 (1993). |
| Remarks | ※Screening of bacterial strains for their ability to metabolize brucine N-oxide (1) Brucine N-oxide (10 mg; 1) in DMSO (0.1ml) was incubated with each bacterial suspension (10 ml) under anaerobic conditions for 4 d and the metabolites were quantitatively analyzed by HPLC using CH3CN-0.03 M Na2HPO4 (45 : 55) as a mobile phase. [El-Mekkawy et al., Planta Med., 59, 347-350 (1993)] ※Incubation of brucine N-oxide (1) with Lactobacillus acidophilus Brucine N-oxide (1,500 mg) was anaerobically incubated for 4d. The residue after the evaporation of solvent was applied to preparative TLC (solvent system B) to isolate metabolites (2 and 3). [El-Mekkawy et al., Planta Med., 59, 347-350 (1993)] |

