|
|
| Compound | Lithospermic acid |
| Animal species | rat |
| Metabolism parameters |
Intravenous administration Intravenous administration |
| Metabolites |
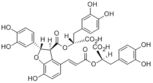
Lithospermic acid B
(R)-2-(((2S,3S)-4-((E)-3-((R)-1-carboxy-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy)-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl)-7-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-3-carbonyl)oxy)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid (R)-2-(((2S,3S)-4-((E)-3-((R)-1-carboxy-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy)-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl)-7-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-3-carbonyl)oxy)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propanoic acid (R)-2-(((E)-3-((2S,3S)-3-(((R)-1-carboxy-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy)carbonyl)-7-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-4-yl)acryloyl)oxy)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propanoic acid (R)-2-(((2S,3S)-4-((E)-3-((R)-1-carboxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)ethoxy)-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl)-7-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-3-carbonyl)oxy)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propanoic acid |
| Crude drug | Lithospermum Root , Salvia Miltiorrhiza Root |
| References | 1) Zhang Y., Akao T., Nakamura N., Duan C. L., Hattori M., Yang X. W., and Liu J. X.: Extremly low bioavailability of magnesium lithospermate B, an active component from Salvia miltiorrhiza, in rat. Planta Med., 70, 138-142 (2004). 2) Zhang Y., Akao T., Nakamura N., Hattori M., Yang X. W., Duan C. L., and Liu J. X.: Magnesium lithospermate B is excreted rapidly into rat bile mostly as methylated metabolites, which are potent antioxidants. Drug Met. Disp. 32, 752-757 (2004). |
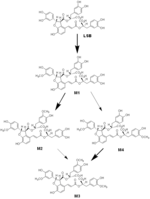
| Remarks | ※Blood sampling Magnesium lithospermate B (MLB) dissolved in saline was injected in a tail vein at 4 or 20 mg/kg. The aqueous solution of MLB was orally given by gastric intubation at 20 or 100 mg/kg. Blood samples were collected from a tail vein (the vein opposite to the injected side in the case of intravenous injection) through heparinized microcapillaries at 5, 10, 20, 40 min, 1, 1.5, 2,3, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 24 h after administration, and centrifuged at 1000 g for 15 min to obtain plasma, which was stored at -30 °C until analysis. [Zhang et al., Planta Med., 70, 138-142 (2004)] ※Bile and urine collection Under light anesthesia with diethyl ether, bile fistulas in 3 or 4 male rats were cannulated with PE-5 polyethylene tubing for collection of bile. The bile was collected into successive vials on ice in 2 ml of 0.1 % H3PO4 at 2-h intervals for 6 h after dosing and in 4 ml of 0.1 % H3PO4 at 4-h intervals for up to 30 h thereafter. Urine was also drawn into a cooled vial over 30 h through a silicone tube (4 mm, i.d.) fixed to the penis. The rats were allowed to recover from anesthesia before receiving a 4-mg/kg intravenous dose of MLB in saline or a 100 mg/kg oral dose of MLB in distilled water. During the period of bile and urine collection, rats were kept in restraining cages with free access to water. All bile and urine samples were stored at -30°C until analysis. [Zhang et al., Drug Met. Disp. 32, 752-757 (2004)] ※Isolation of biliary metabolites Bile from 16 rats with biliary fistulization for 10 h after bolus intravenous injection at a dose of 25 mg/kg was combined, diluted with water to 200 ml, and applied to a Diaion HP-20 (porous polymer resin, aromatic type absorbents based on crosslinked polystyrenic matrix) column. After washing with 800 ml of water, the column was eluted with MeOH-H2O (700 ml with 1:4 and 1000 ml with 3:2, respectively). Further repeated column chromatography using Wakogel 100C18, which was eluted with 0.1% TFA-MeOH, afforded Ml (80 mg), M2 (40 mg), M3 (11 mg), and M4 (2 mg) as free acid forms. The purity of each metabolite was 97, 98, 90, and 90%, respectively, based on HPLC analyses. [Zhang et al., Drug Met. Disp. 32, 752-757 (2004)] |

