|
|
| Compound | Aucubin |
| Animal species | human intestinal microflora |
| Metabolism parameters | |
| Metabolites |
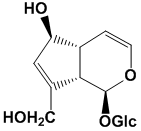
Aucubin
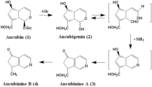
Aucubigenin (1S,4S,5R)-4-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-5-((Z)-2-hydroxyvinyl)cyclopent-2-enecarbaldehyde (4aR,5S,7aS)-7-(hydroxymethyl)-5,7a-dihydro-4aH-cyclopenta[c]pyridin-5-ol Aucubinine A Aucubinine B |
| Crude drug | Eucommia Bark , Plantago Herb , Plantago Seed , Processed Rehmannia Root , Rehmannia Root |
| References | 1) Hattori M., Kawata Y., Inoue K., Shu Y. Z., Che Q. M. and Namba T. and Kobashi K.: Transformation of aucubin to new pyridine monoterpene alkaloids, aucubinines A and B, by human intestinal bacteria. Phytother. Res., 4, 66-70 (1990). |
| Remarks | ※Incubation of aucubin with Bacteroides fragilis A strain of B. fragilis was anaerobically cultured in GAM broth (50 mL x 5) for 20 h at 37 °C in an anaerobic jar, in which air had been replaced by oxygen-free CO2 gas in the presence of steel wool (steel wool method). The culture was centrifuged at 5700 x g for 5 min. The precipitates were washed with a saline solution and suspended in 0.1M phosphate buffer (pH 7.4, 200 mL). Aucubin (200 mg, 1) was then added. The mixture was anaerobically incubated for 12 h at 37 °C and extracted with water-saturated BuOH (50 mL x 3). The combined BuOH solutions were pooled and evaporated in vacuo to give an oily residue. The residue was applied to a column of silica gel (45 cm x 2.1 cm ID). The column was eluted with hexane, hexane + CHCl3, and CHCl3 with in creasing amounts of MeOH. Three metabolites (A1, A2 and A3) obtained from these fractions were further purified by repeating preparative TLC. [Hattori et al., Phytother. Res., 4, 66-70 (1990)] ※Incubation of aucubin (1) with a mixture of human intestinal bacteria a) Sixty mL of a bacterial mixture from human feces containing aucubin (100 mg, 1) was incubated for 18 h at 37 °C. The EtOAc extract (20 mL x 4) contained aucubinines A (3) and B (4), which were identified by comparison of the chromatographic behavior and spectral properties with those of authentic samples. b) One mL of the bacterial mixture was inoculated into 100 mL of GAM broth and anaerobically cultured for 18 h at 37 °C. The culture was then centrifuged to collect the bacterial cells. After washing with a saline solution, the cells were suspended in 40 mL of 100 mM phosphate buffer. Aucubin (100 mg, 1) was added to the suspension. The mixture was incubated for 24 h at 37 °C and extracted with EtOAc (20 mL x 4). Aucubinines A (3) and B (4) were detected in the extract by TLC. [Hattori et al., Phytother. Res., 4, 66-70 (1990)] |

