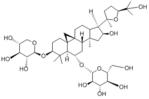
|
| Compound | Cycloastragenol |
| Animal species | Caco-2 cell, rat and human hepatic microsome |
| Metabolism parameters | |
| Metabolites |
AstragalosideⅣ
Cycloastragenol |
| Crude drug | Astragalus Root |
| References | 1) Zhu J, Lee S, Ho MK, Hu Y, Pang H, Ip FC, Chin AC, Harley CB, Ip NY, and Wong YH.: In vitro intestinal absorption and first-pass intestinal and hepatic metabolism of cycloastragenol, a potent small molecule telomerase activator. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet., 25:477-86 (2010). 2) Wen XD, Qi LW, Li P, Bao KD, Yan XW, Yi L, and Li CY.: Simultaneous determination of calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside, ononin, astragaloside IV, astragaloside I and ferulic acid in rat plasma after oral administration of Danggui Buxue Tang extract for their pharmacokinetic studies by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci., 865: 99-105 (2008). 3) Zhang Q, Zhu LL, Chen GG, and Du Y.: Pharmacokinetics of astragaloside iv in beagle dogs. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 32: 75-9 (2007). |
| Remarks | ※Approximate 87% of initially applied cycloastragenol (CAG) remained unchanged after 6 h incubation with Caco-2 culture. However, CAG underwent extensive hepatic phase I metabolism as revealed in liver microsome-mediated degradation. |

